Quick Details
Material: F51 (2205/UNS S31803/UNS S32205)
Technics: Cold forming
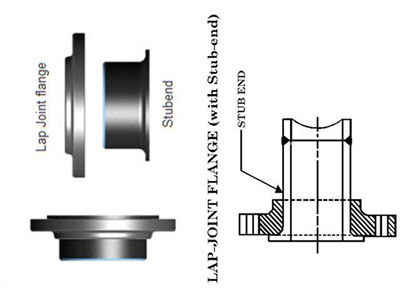
Type: Stub End
Place of Origin: Zhejiang, China (Mainland)
Brand Name: Tanell
Connection: Welding
Head Code: Round
Size: 14" (DN350)
Products
Credibility ,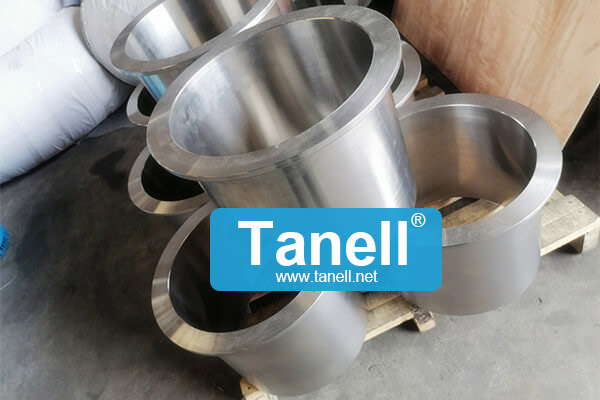


Material: F51 (2205/UNS S31803/UNS S32205)
Technics: Cold forming
Type: Stub End
Place of Origin: Zhejiang, China (Mainland)
Brand Name: Tanell
Connection: Welding
Head Code: Round
Size: 14" (DN350)
| Packaging Details: | fumigation free plywood cases or as per customers' requests |
|---|---|
| Delivery Detail: | Delivery after receiving deposit |
ASME B16.9 ASTM A815 F51 Welded Lap Joint Stub End 14 Inch Schedule STD
Size: 14" (DN350)
Thk: Sch STD
Material: F51 (2205/UNS S31803/UNS S32205)
China STUB END Manufacturer Tanell offers ASME B16.9 ASTM A815 F51 Welded Lap Joint Stub End, 14 Inch, Schedule STD.
UNS S31803 and UNS S32205 are commonly referred to as Duplex 2205 material, whose “Duplex” name is derived from the mixed microstructure which contains about equal portions of ferrite and austenite. Developed more than 70 years ago in Sweden precisely for the sulfite paper industry where the Duplex’s were used to combat corrosion problems caused by chloride-bearing cooling waters and other aggressive chemical products. Since then there have been advancements in the composition such as the deliberate addition of nitrogen as an alloying agent, which afterwards quickly made Duplex the “workhorse” of stainless steels.
Generally, UNS S31803 has been solely designated to the Duplex 2205 grade. More recently, it has been available complying with the higher corrosion resistant composition UNS S32205. The only difference in the UNS numbers is that UNS S32205 contains a higher nitrogen content which guarantees better corrosion resistance. Composed of between 21% to 23% chromium, 4.5% to 6.5% nickel, 5% to 3.5% molybdenum, 2% manganese, and 1% silicon, with the balance being iron. Also found in Duplex Stainless Steel are trace amounts of carbon, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen.
Chemical Properties of F51 (2205/UNS S31803/UNS S32205):
C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N | |
2205 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.03 | 0.02 | min: 21.0 | min: 2.5 | min: 4.5 | min: 0.08 |
2205 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.03 | 0.02 | min: 22.0 | min: 3.0 | min: 4.5 | min: 0.14 |
Mechanical Properties of F51 (2205/UNS S31803/UNS S32205):
Grade | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Elongation % | Hardness (HB) MAX |
2205 | 90 | 65 | 25 | 217 |
Physical Properties of F51 (2205/UNS S31803/UNS S32205):
Density | Electrical | Thermal | Heat | Electrical | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
at 68°F | 0.278 | 27.6 | 8.7 | 0.112 | 33.5 |
at 212°F | 26.1 | 9.2 | 0.119 | 35.4 | |
at 392°F | 25.4 | 9.8 | 0.127 | 37.4 | |
at 572°F | 24.9 | 10.4 | 0.134 | 39.4 |
Type | F51 Welded Stub End |
Standard | ASME B16.9, MSS SP-43, HG205099, HG20621, GB/T12459-2005, GB/T13401, SH3408-96,etc. |
Size | 1/2"-48"(DN15-DN600) |
Wall thickness | SCH5S-SCH40S |
Type | Type A, Type B,Type C |
Surface treatment | Lathe finish&Abrasive blasting |
Stainless steel | 304, 304L,304H, 316, 316L,309S,310S, 321,321H,347H,316Ti |
Duplex steel | 2205, etc |
Super duplex steel | 2507, etc |
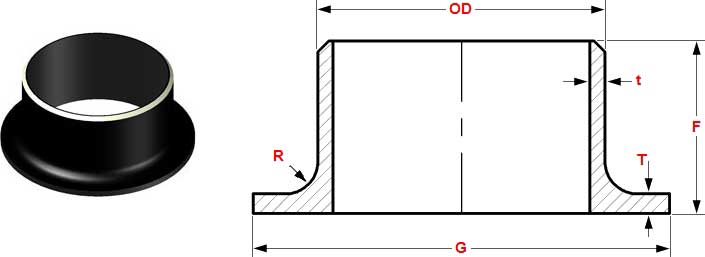
| NPS | OD | T | G | F | R | kg |
| 4 | 114.3 | 6.02 | 157.2 | 152.4 | 11.11 | 3 |
| 5 | 141.3 | 6.55 | 185.7 | 203.2 | 11.11 | 5.4 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 7.11 | 215.9 | 203.2 | 12.70 | 7.3 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 8.18 | 269.9 | 203.2 | 12.70 | 11.6 |
| 10 | 273.1 | 9.27 | 323.9 | 254 | 12.70 | 18 |
| 12 | 323.9 | 9.53 | 381 | 254 | 12.70 | 21 |
| 14 | 355.6 | 9.53 | 412.8 | 304.8 | 12.70 | 28 |
| 16 | 406.4 | 9.53 | 469.9 | 304.8 | 12.70 | 34 |
| 18 | 457.2 | 9.53 | 533.4 | 304.8 | 12.70 | 39 |
| 20 | 508 | 9.53 | 584.2 | 304.8 | 12.70 | 44 |
| 24 | 609.6 | 9.53 | 692.2 | 304.8 | 12.70 | 57 |
Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated. Weights are in kilograms and approximately given.
| Nominal Pipe Size | 1/2 up to 2.1/2 | 3 to 3.1/2 | 4 | 5 to 8 | 10 to 18 | 20 to 24 |
| Outside Diameter at Welding End (OD) | + 1.6 - 0.8 | 1.6 | 1.6 | + 2.29 - 1.6 | + 4.06 - 3.05 | + 6.35 - 4.83 |
| Overall Length (F) | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2 | 2 |
| Outside Diameter of Lap (G) | + 0 - 0.76 | + 0 - 0.76 | + 0 - 0.76 | + 0 - 0.76 | + 0 - 1.6 | + 0 - 1.6 |
| Thickness of Lap (T) | + 1.52 - 0 | + 1.52 - 0 | + 1.52 - 0 | + 1.52 - 0 | + 1.52 - 0 | + 1.52 - 0 |
| Fillet Radius of Lap (R) | + 0 - 0.76 | + 0 - 0.76 | + 0 - 1.6 | + 0 - 1.6 | + 0 - 1.6 | + 0 - 1.6 |
| Wall Thickness (t) | Not less than 87.5% of Nominal Wall Thickness | |||||
Dimensional tolerances are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
Benefits of Duplex include: good weldability and workability, high resistance to corrosion fatigue, stress corrosion cracking (especially chloride stress corrosion cracking), erosion, and high energy absorption. Other advantages of Duplex are higher heat conductivity and low thermal expansion compared to austenitic stainless steels, high strength, good resistance to sulfide stress corrosion, and high resistance to pitting and crevice to corrosion. Duplex 2205® accounts for over 80% of the total usage of Duplex stainless steels throughout the world because of its superior workability as well as corrosion resistance.
Possesses good weldability
Should not generally be welded without filler metal as this may result in excessive ferrite
Annealing temperature range is 1868 to 2012°F (1020 to 1100°C)
Cannot be hardened by heat treatment – but Duplex 2205 does work-harden
Special consideration is needed to compensate for a higher coefficient of thermal expansion to avoid warping and distortion
Most Duplex 2205 producers recommend a maximum hot forming temperature between 2010 and 2100°F (1100 to 1150°C). If the shape of the work piece is not compact, the edges may be significantly cooler than the bulk, and there is risk of cracking in the cooler regions.
Duplex 2205 has shown good formability in a variety of fabrications. The high strength of Duplex 2205 can pose problems. Even when the equipment has sufficient power, allowance must be made for higher spring-back caused by the grade’s high strength.
Duplex 2205 is somewhat more difficult to machine than the 300 series austenitic stainless steels. Higher cutting forces are required and more rapid tool wear is typical. Some guidelines for machining are: A) Use powerful, rigid machines with extremely strong rigid mounting of tools and work piece, B) Minimize vibration by keeping the tool extension as short as possible, C) Use a nose radius on the tool, no longer than necessary, for carbides that have a sharp edge while still providing adequate strength, D) Design machining sequences to always provide for a depth of cut below the work hardened layer resulting from the previous passes.
Chemical processing, transport and storage – pressure vessels, tanks, piping, and heat exchangers
Oil and gas exploration and processing equipment – piping, tubing, and heat exchangers
Marine and other high chloride environments
Effluent scrubbing systems
Pulp and paper industry – digesters, bleaching equipment, and stock-handling systems
Cargo tanks for ships and trucks
Food processing equipment
Biofuels plants
ASTM/ASME: A240 UNS S32205/S31803
EURONORM: 1.4462 X2CrNiMoN 22.5.3
AFNOR: Z3 CrNi 22.05 AZ
DIN: W.Nr 1.4462
You can visit this website: tanell.net(Zhejiang Tanell Pipes&Fitting Co., Ltd)

Tel:+86-577-85982258 / Email:tan@tanell.com
Address:NO.568-D Three Street Three Road,Binhai Wenzhou Zhejiang
COPYRIGHT©2024 tanell.net Zhejiang Tanell Pipes&Fitting Co., Ltd
Tanell is an company that operates in the supplying market for Oil and Gas plant, Chemical industry, Energy and Water since 1981.